
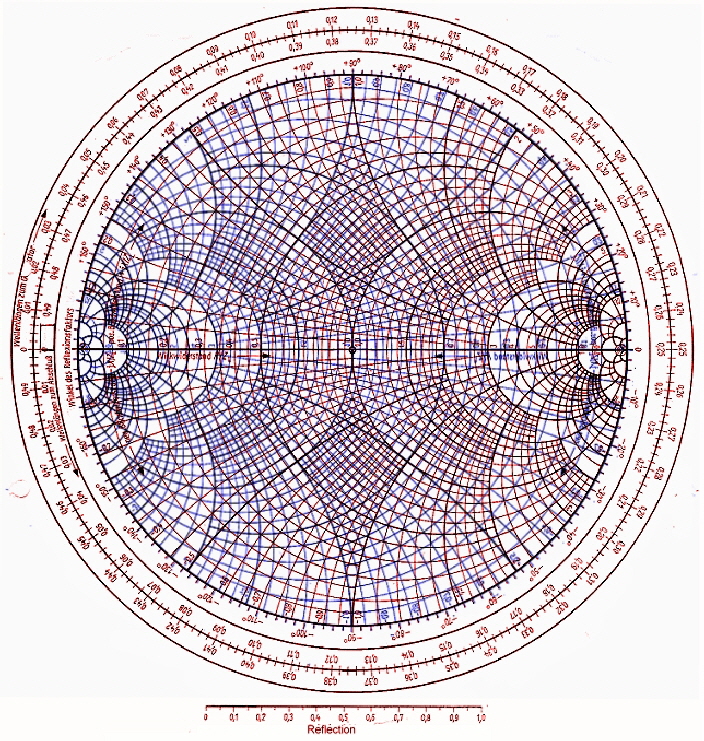
The point marked 1.0 on the resistance axis is called the prime center of the Smith Chart, so we say that the process of normalization with regard to a Smith chart refers to reassigning impedance values with regard to the prime center. A reactance of 50 + j100 would be plotted on the resistance circle going through the prime center where it intersects the reactance arc marked 2.0. What this means is that if you’re working with a 50 ohm transmission line, you’d normally divide the impedances by 50, meaning that a 50 ohm resistance would then be plotted on the resistance axis at the point marked 1.0. When you work with a Smith Chart, you use resistance and reactance values that are normalized to the characteristic impedance of the system. QUESTION: On the Smith chart shown in Figure E9-3, what is the name for the large outer circle on which the reactance arcs terminate? (E9G06) QUESTION: What do the arcs on a Smith chart represent? (E9G10) When oriented so that the resistance axis is horizontal, positive reactances are plotted above the resistance axis and negative reactances below. Points on the reactance axis have a resistance of 0 ohms.
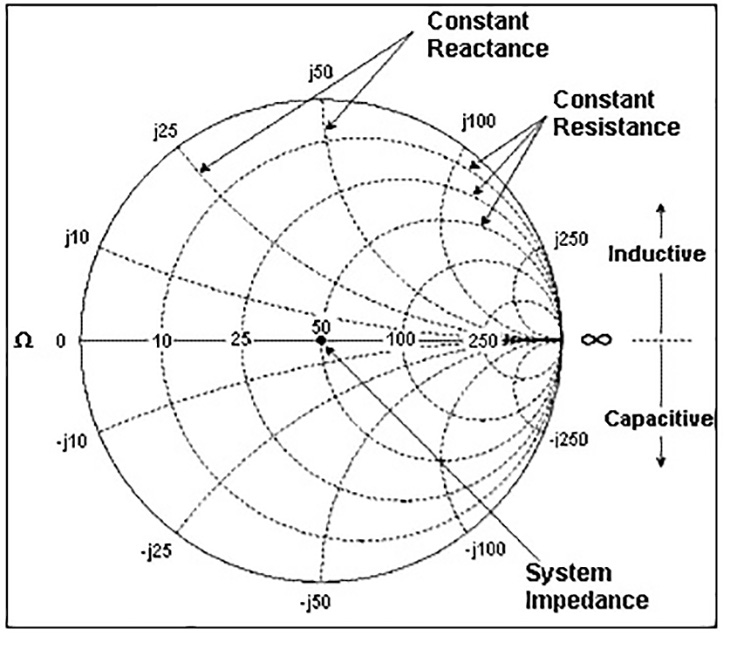
The arcs on a Smith chart represent points with constant reactance, and the large outer circle on which the reactance arcs terminate is called the reactance axis. QUESTION: On the Smith chart shown in Figure E9-3, what is the only straight line shown? (E9G07) QUESTION: What are the two families of circles and arcs that make up a Smith chart? (E9G04) QUESTION: What type of coordinate system is used in a Smith chart? (E9G02)ĪNSWER: Resistance circles and reactance arcs In practice, you want to position the chart so that 0 ohms is at the far left, while infinity is at the far right. Points on this axis are pure resistances. The resistance axis is the only straight line on the Smith chart. The Smith chart coordinate system is comprised of resistance circles and reactance arcs. While a complete discussion of the theory behind the Smith Chart is outside the scope of this study guide, a good discussion of the Smith Chart can be found on the ARRL website. A Smith chart, shown in Figure E9-3 above, is a chart designed to solve transmission line problems graphically.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
